Introduction to Slump Concrete Definition
Concrete is one of the most essential materials used in construction, from residential buildings to large infrastructure projects. Its quality, workability, and consistency directly affect the durability and safety of the structures it forms. One of the primary measures of concrete’s workability is the slump test, which allows engineers to evaluate how fluid or stiff a mix is before it sets. Understanding slump concrete definition is crucial for anyone involved in construction, as it provides insights into how the material will behave during transportation, placement, and compaction. The test offers a simple, reliable method to ensure concrete consistency and helps prevent problems such as segregation, honeycombing, or weak structural zones.
The Concept of Slump Concrete Definition
Slump concrete definition refers to the measure of concrete’s consistency in its fresh state. Specifically, it is the vertical subsidence or settlement of freshly mixed concrete when a standard mold, known as an Abrams cone, is removed. This measure indicates how workable the concrete is, which is vital for placement and compaction. By defining slump concrete, engineers and construction professionals can quickly identify whether a mix is too stiff, too fluid, or within the ideal range. A proper slump ensures that concrete can fill formwork completely, encase reinforcement effectively, and achieve the required strength after curing.
Purpose of Slump Testing
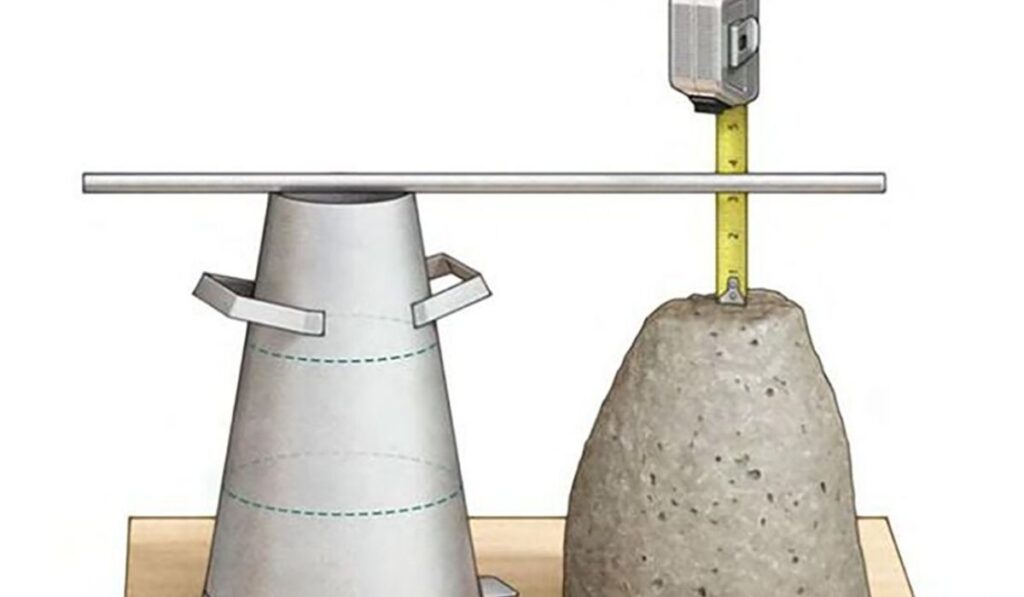

The primary purpose of conducting a slump test is to define slump concrete consistency and ensure uniformity across different batches. Variations in water content, cement proportions, or aggregate grading can lead to inconsistencies that affect strength and durability. A slump test provides immediate feedback, allowing adjustments to be made on-site if necessary. It also serves as a quality control measure, helping contractors meet design specifications and avoid costly defects. Understanding slump concrete definition is therefore not only about measuring workability but also about maintaining construction quality and reliability.
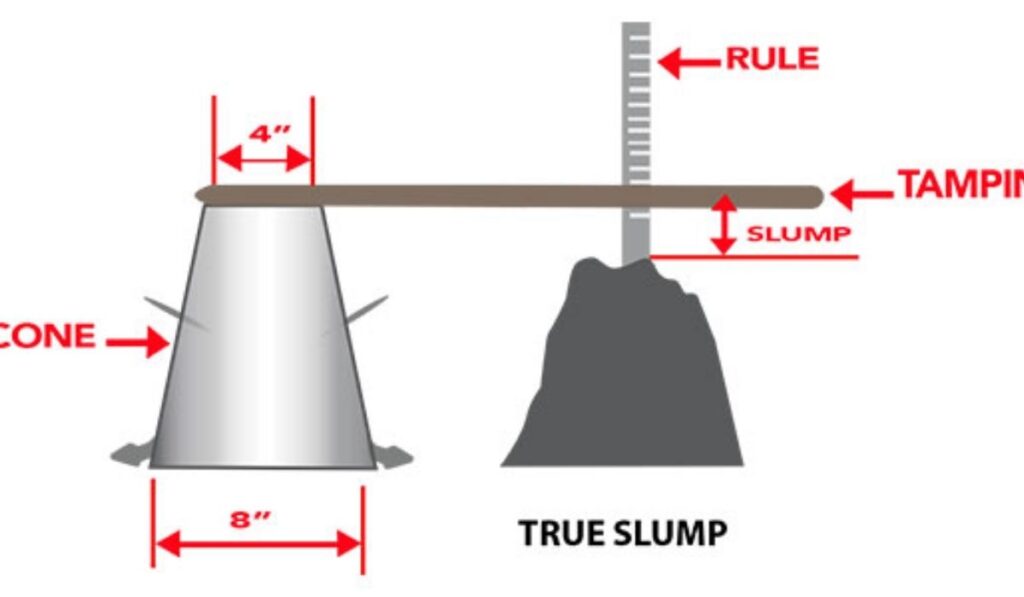
Equipment Required for Slump Test
Performing a slump test requires simple yet standardized equipment. The main tool is the slump cone, or Abrams cone, which has specific dimensions and a smooth internal surface. Additional tools include a tamping rod, a base plate, and a measuring scale to record the vertical slump. Using the proper equipment ensures consistent results and allows engineers to define slump concrete with accuracy. Each tool contributes to a controlled testing environment, eliminating variables that might affect the interpretation of the concrete’s workability.
Procedure of Slump Test
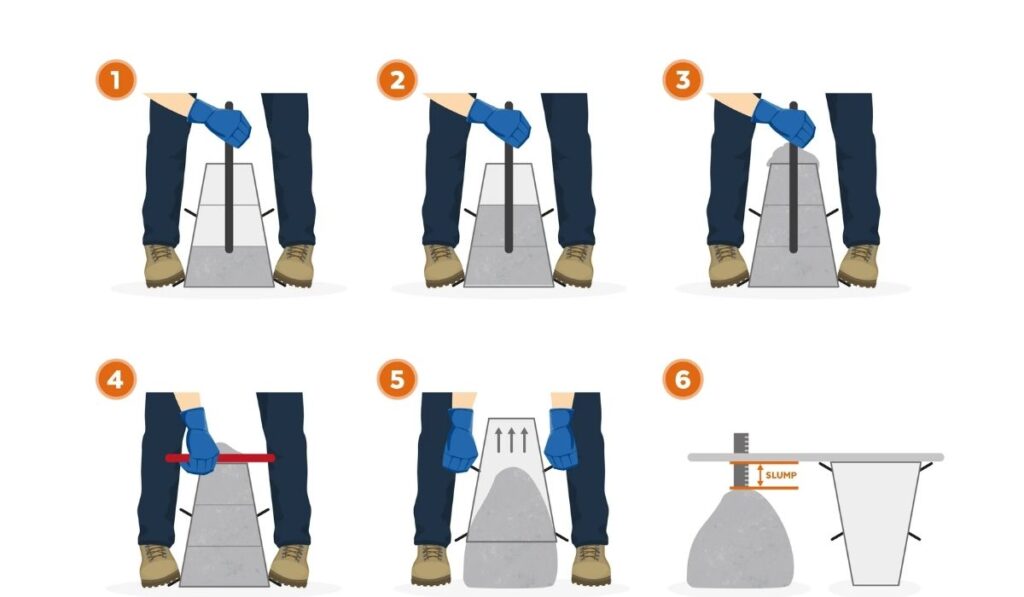
The slump test procedure follows standardized steps to define slump concrete effectively. Freshly mixed concrete is placed into the slump cone in three layers, each layer compacted using the tamping rod. After filling and leveling the cone, it is carefully lifted, allowing the concrete to settle. The vertical distance between the height of the cone and the top of the settled concrete is measured as the slump. This measurement indicates the consistency and workability of the concrete mix. Observing the slump pattern also helps identify potential problems such as segregation, low cohesion, or excessive water content.
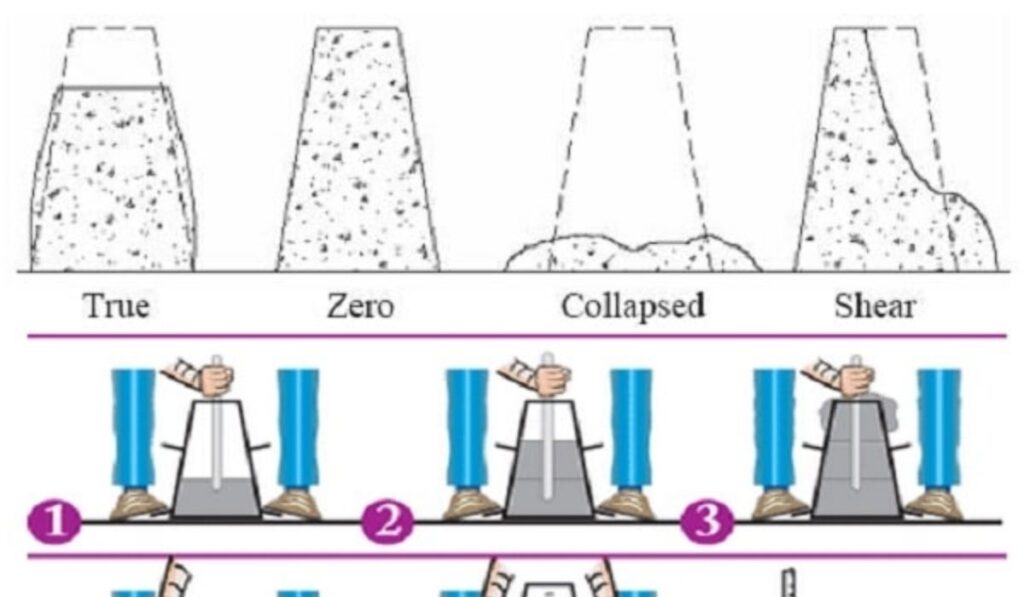
Types of Slump
Different slump patterns provide additional information about the concrete mix. A true slump occurs when the concrete settles evenly without significant deformation, indicating ideal workability. A shear slump happens when one side collapses, often due to low cohesion, while a collapse slump occurs when the concrete is overly wet and flows excessively. Understanding these variations helps engineers define slump concrete beyond a numeric value, offering insight into the mix’s behavior under field conditions. This knowledge ensures that the concrete performs reliably during placement and compaction.
Factors Affecting Slump Concrete
Several factors influence slump concrete definition, making careful interpretation essential. Water content is the most significant factor, as small changes can dramatically alter workability. Aggregate size, shape, and grading also affect slump, as does cement content and admixtures like plasticizers. Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can further impact slump measurements. By understanding these factors, construction professionals can accurately define slump concrete and adjust mix proportions to achieve the desired workability while maintaining strength and durability.
Importance in Construction Quality
Properly defining slump concrete is critical for construction quality. If the slump is too low, the concrete may be difficult to place and compact, leading to honeycombing and poor bonding with reinforcement. If the slump is too high, excess water can weaken the mix, reduce durability, and increase shrinkage and cracking. By monitoring slump regularly, contractors can ensure consistency across pours, improve structural integrity, and prevent defects. Slump concrete definition therefore serves as a practical indicator of both fresh concrete behavior and long-term performance.
Standards and Specifications
International standards such as ASTM C143 and EN 12350-2 provide guidelines for slump testing to define slump concrete consistently. These standards specify cone dimensions, compaction methods, and measurement techniques to ensure repeatable results. Designated slump ranges depend on application type, with lower slump recommended for foundations and high-strength applications and higher slump acceptable for lightly reinforced structures or slabs requiring easier placement. Following these standards ensures that construction practices meet industry requirements and maintain safety and durability.
Limitations of Slump Test
While slump testing is valuable, it has limitations. It is primarily suited for conventional concrete mixes and may not accurately reflect the workability of self-compacting or highly flowable concrete. The test does not directly measure strength, durability, or other hardened concrete properties. Nonetheless, understanding slump concrete definition and combining it with additional tests like compressive strength, air content, and flow table tests provides a comprehensive quality control framework. Awareness of these limitations allows engineers to interpret results correctly and make informed decisions.
Applications of Slump Testing
Slump testing is widely used in field construction, ready-mix operations, and laboratory settings. It allows contractors to monitor consistency during transportation, verify compliance with design specifications, and ensure uniformity across multiple batches. By defining slump concrete on-site, teams can take immediate corrective action if a mix is too wet or too dry. This proactive approach minimizes waste, reduces structural defects, and supports efficient construction practices. The test also serves as a communication tool between engineers, contractors, and suppliers, ensuring that everyone is aligned on concrete quality expectations.
Final Thoughts on Slump Concrete Definition
Understanding and defining slump concrete definition is fundamental for quality control in modern construction. The slump test provides a simple, reliable method to evaluate workability, guide mix adjustments, and maintain consistency across projects. While it does not measure strength or durability directly, it offers immediate insight into concrete performance in its fresh state. Contractors, engineers, and quality control teams rely on this test to prevent defects, ensure compliance with specifications, and deliver durable, safe structures.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does slump concrete definition mean?
- It refers to the measure of fresh concrete’s consistency and workability.
2. Why is slump testing important?
- It ensures concrete can be placed and compacted properly, preventing defects.
3. What equipment is needed for a slump test?
- A slump cone, tamping rod, base plate, and measuring scale.
4. What factors affect slump measurements?
- Water content, aggregates, admixtures, cement proportion, and temperature.
5. Can slump test predict concrete strength?
- No, it only measures workability, not the hardened concrete’s strength.








