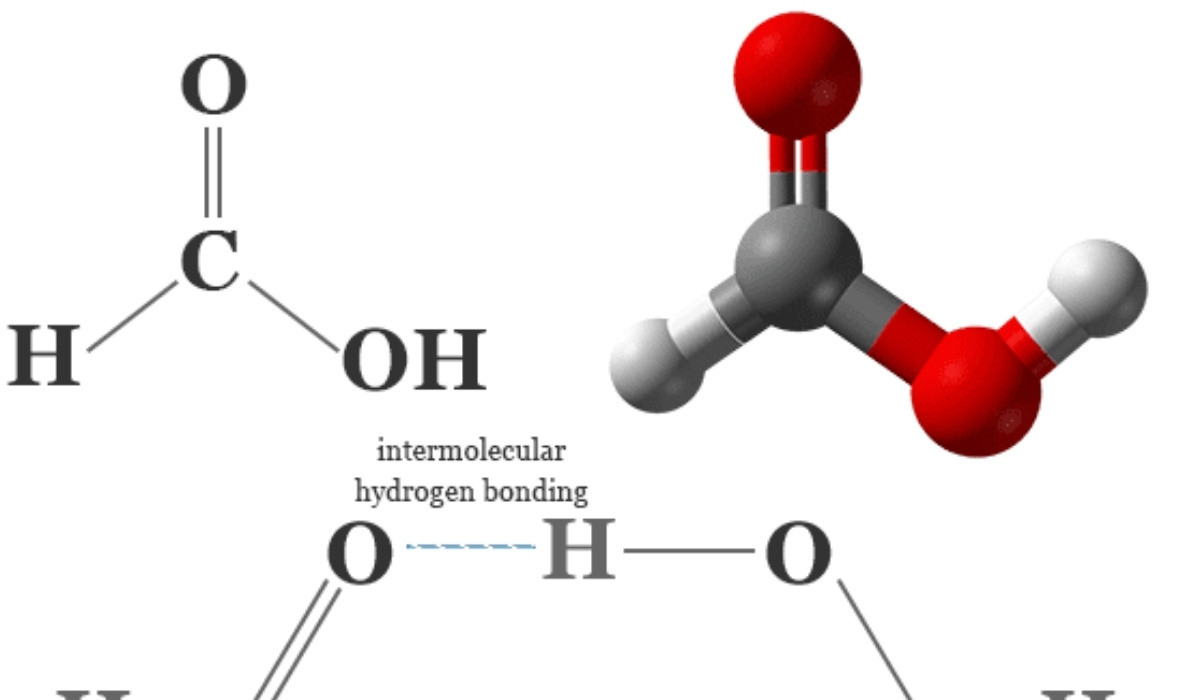
The study of simple organic molecules forms the foundation of chemistry because these compounds illustrate how atomic structure determines behavior and reactivity. Among such molecules, formic acid and its related molecular interactions with other small compounds offer a clear window into chemical bonding principles. Discussions surrounding hcooh structure are especially important because they connect molecular geometry with acidity polarity and chemical function. By examining how atoms are arranged and how they interact, students and researchers gain insight into why this compound behaves the way it does in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Understanding molecular structure also helps explain how small organic acids participate in reactions ranging from esterification to biological processes. The combination of formic acid with related molecules highlights hydrogen bonding intermolecular forces and electron distribution. These concepts are not abstract theories but practical tools used in chemical analysis and material science.
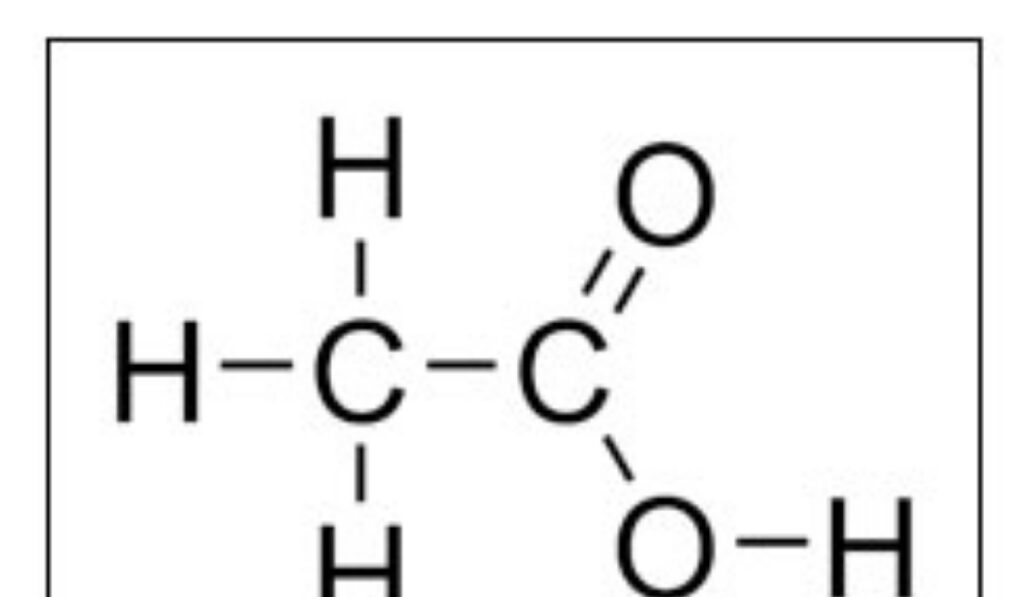
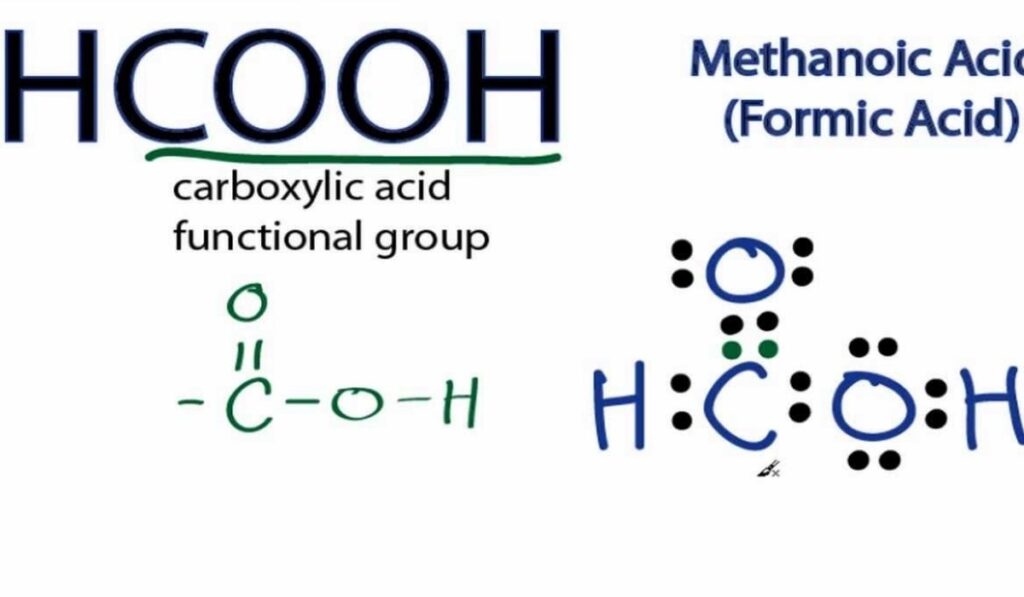
Basic Composition of Formic Acid
Formic acid is one of the simplest carboxylic acids and serves as an excellent model for understanding organic acid behavior. Its molecular formula reflects a carbon atom bonded to both a hydrogen atom and a carboxyl group. The simplicity of this arrangement makes hcooh structure an ideal teaching example for introducing functional groups in organic chemistry.
The carbon atom sits at the center of the molecule and forms bonds with oxygen and hydrogen atoms in a specific geometric arrangement. This configuration determines not only the shape of the molecule but also its polarity and reactivity. The presence of oxygen atoms creates regions of partial negative charge that influence how the molecule interacts with solvents and other chemicals.
Molecular Geometry and Bonding
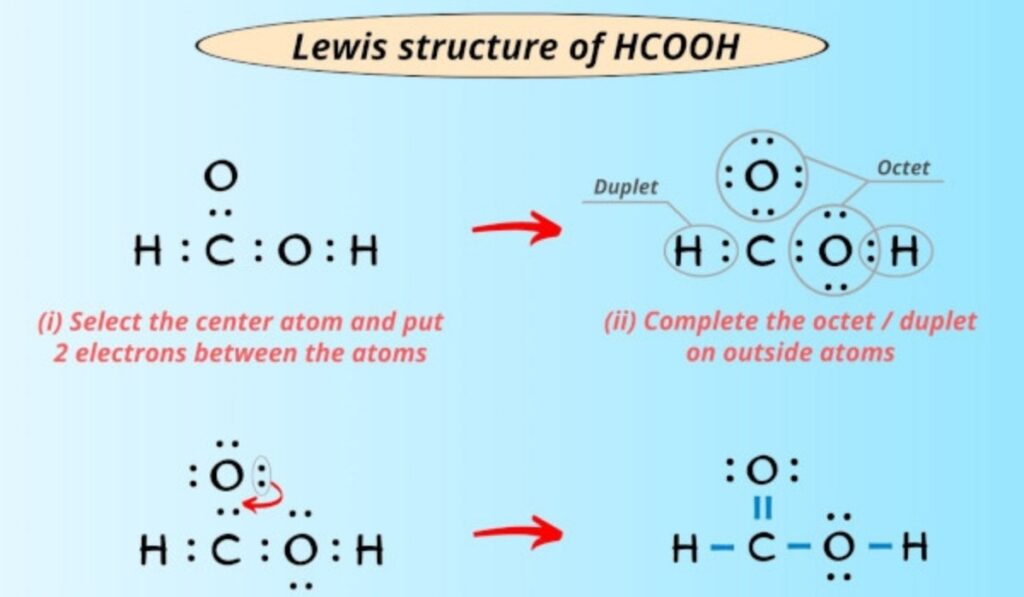
The geometry of formic acid is dictated by electron pair repulsion and orbital hybridization. The central carbon atom adopts a planar arrangement that allows optimal overlap of orbitals. This geometry is a defining feature of hcooh structure and explains why the molecule behaves predictably in reactions involving nucleophiles and electrophiles.
Bond lengths and angles within the molecule reflect the balance between single and double bond character. Resonance plays a role in distributing electron density across the carboxyl group, stabilizing the molecule and enhancing its acidic nature. These structural features are essential for understanding why formic acid readily donates a proton in aqueous environments.
Hydrogen Bonding and Intermolecular Forces
Hydrogen bonding is one of the most significant intermolecular interactions associated with formic acid. The oxygen atoms within the molecule can both donate and accept hydrogen bonds, leading to strong attractions between neighboring molecules. This aspect of hcooh structure explains many of its physical properties, including boiling point and solubility.
In mixtures involving water or other polar solvents, hydrogen bonding allows formic acid molecules to integrate smoothly into the solvent network. This behavior is critical for its use in chemical synthesis and industrial processes where controlled solubility is required.
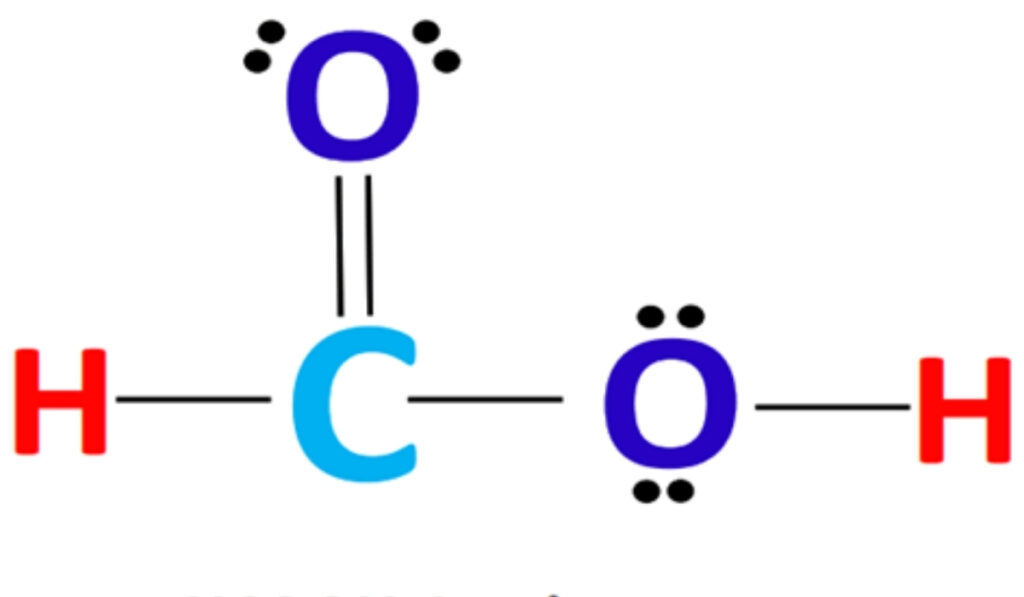
Interaction with Water Molecules
When formic acid interacts with water, the molecular structure facilitates proton transfer and hydration. The orientation of oxygen atoms allows water molecules to stabilize the charged species formed during dissociation. This interaction is closely tied to hcooh structure and helps explain the compound’s acidic strength relative to other small organic acids.
The formation of hydrogen bonded networks in aqueous solutions influences conductivity and reaction kinetics. These properties are especially relevant in analytical chemistry and biochemical contexts where precise control of acidity is essential.
Chemical Properties Linked to Structure
The chemical behavior of formic acid is directly linked to its molecular arrangement. Its acidity arises from the stability of the conjugate base, which is enhanced by resonance within the carboxyl group. Understanding hcooh structure allows chemists to predict how the molecule will behave under different conditions.
Reactivity patterns such as oxidation reduction and ester formation can all be traced back to electron distribution within the molecule. Structural analysis therefore serves as a predictive tool rather than a purely descriptive exercise.
Role in Organic Chemistry Reactions
Formic acid plays a role in various organic reactions including reduction processes and as a reagent in synthesis pathways. Its small size and reactive functional group make it versatile. The predictable nature of hcooh structure ensures consistent behavior in controlled reactions.
In teaching laboratories, formic acid is often used to demonstrate principles of acidity and reaction mechanisms. Its structure allows students to visualize how theoretical concepts apply to real chemical systems.
Industrial and Practical Uses
Beyond the laboratory, formic acid has numerous industrial applications. It is used in leather processing textile treatment and as a preservative. The effectiveness of these applications is tied to hcooh structure which governs reactivity and interaction with materials.
Its ability to break down under certain conditions also makes it useful in environmentally conscious processes. Understanding structure enables safer handling and optimized use in industrial contexts.
Biological and Environmental Significance
Formic acid occurs naturally in various biological systems and plays a role in metabolic pathways. Ant venom and certain plant processes rely on its chemical properties. These biological functions are rooted in hcooh structure and its interaction with enzymes and tissues.
In environmental chemistry, formic acid participates in atmospheric reactions and influences acidity in rainwater. Structural knowledge helps scientists model these processes accurately.
Importance of Structural Understanding in Chemistry Education
Studying molecular structure builds a bridge between theory and application. Formic acid serves as a foundational example that illustrates key principles without unnecessary complexity. Mastery of hcooh structure equips learners with tools applicable to more complex molecules.
By focusing on structure, chemistry education moves beyond memorization toward true understanding. This approach fosters analytical thinking and prepares students for advanced study and research.
Frequently Asked Questions
One What does hcooh structure represent
- It describes the atomic arrangement and bonding within formic acid
Two Why is formic acid considered a simple organic acid
- Because it contains the smallest possible carboxyl group structure
Three How does structure affect acidity
- Electron distribution and resonance stabilize the conjugate base
Four Is hydrogen bonding important for formic acid
- Yes it strongly influences physical and chemical properties
Five Where is formic acid commonly used
- It is used in laboratories industries and natural biological systems